Resource Centre
ASLM’s Resource Center is designed to help you keep up with the latest tool kits, regulations, guides and other information published by ASLM, partners, and global health regulatory bodies. Use the filters above to locate the information you need based on the ASLM project, resource type, or topic of interest.
These presentation slides are from the Women-Centered Diagnostics satellite session of the 2019 International Conference on AIDS and STIs in Africa (ICASA 2019) that was jointly organized by the African Society for Laboratory Medicine (ASLM), the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI), the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation (EGPAF), UNICEF and Unitaid. Much has been done… Read More
To reach the third 90 of the UNAIDS 90–90–90 targets, country programmes must delve into their data and understand how they represent the quality of VL testing services. This guide, published by WHO, presents key considerations and examples of tools (provided in the annexes) to assist countries in developing a national VL M&E plan. As… Read More
The guidelines for the Stepwise Laboratory Quality Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (SLIPTA), published by WHO, provides a framework for countries in the Africa Region in their efforts to strengthen medical laboratory services through fulfilment of the requirements of the ISO 15189 standard. The SLIPTA Guideline describes key elements of the laboratory quality improvement process and… Read More
The SLIPTA Checklist, published by WHO, specifies requirements for quality and competency, aimed to develop and improve medical laboratory services to raise laboratory quality to established national and/or international standards. Laboratories will receive a 0-5 star level rating to certify that the audited laboratory is undergoing the quality improvement process to meet all the requirements… Read More
Use the Accredited Laboratories Distribution Map to see the distribution of Internationally Accredited laboratories and the detailed information of each specific country
The African Society for Laboratory Medicine (ASLM) has been designated by WHO-AFRO in October 2012 to coordinate and lead the implementation of the Stepwise Quality Laboratory Improvement Process towards Accreditation (SLIPTA) in Africa. ASLM has then developed a standardized SLIPTA auditor training curricula and trained the training at a country and regional levels. The training… Read More
Welcome to the point-of-care (POC) early infant diagnostic (EID) landscape in Africa. Through funding provided by Unitaid, partners including the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI), UNICEF, and ASLM have successfully supported the introduction of POC EID and viral load (VL) technologies and pilot activities in sub-Saharan African countries. Strategic deployment of POC EID is key… Read More
Use the SLIPTA Audited Laboratories Distribution Map to see the distribution of SLIPTA laboratories and the detailed information of each specific country
The purpose of this tool is to assist in identifying gaps and creating awareness of best practices for waste management processes in VL and EID molecular testing laboratories (and associated healthcare facilities), in order to provide a starting point for assistance in waste mitigation strategies. This tool is for completion by site managers, safety managers,… Read More
The September 2019 IDC meeting was convened to review the activities carried out since the previous meeting on September 2018, discuss proposed next steps, and outline a plan of action for the next 12 months. The meeting objectives were to: Review the outputs from all work-streams and define a consensus position by the consortium, where… Read More
Diagnostic network optimization is an exercise that aims to redesign the diagnostic network set-up in order to increase access, maximize impact, and generate efficiencies. It aligns testing demand and capacity in the most cost-effective way by defining the optimal instruments mix, identifying the most appropriate locations where instruments should be placed, and designing the referral… Read More
WHO has produced a biosafety video series entitled, “Good Microbiological Practice and Procedures (GMPP)”, which is central to the WHO Laboratory Biosafety Manual (LBM4) being revised and finalised. These seven training videos will help enhance the safety of any health laboratory, including those in resource-limited settings.
With limited funding for global health, identifying practical, cost and timesaving solutions, while also ensuring quality of care is increasingly important. One approach to increasing access to Point-of-Care testing is integrated testing (a term often used interchangeably with “multi-disease testing”), which tests for different conditions or diseases using the same diagnostic platform. This brief summarizes… Read More
This Fact Sheet gives the situation as of July 2019 of the Status of HIV self-testing (HIVST) in national policies, implementation of Treat All ART recommendation among adults and adolescents living with HIV, implementation of Treat All policy for pregnant and breastfeeding women living with HIV, national policy on routine viral load testing for monitoring… Read More
Increased access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) and treatment monitoring for pregnant and breastfeeding women living with HIV is a priority for promoting health during the pregnancy and post-partum periods, and to minimize the risk of vertical transmission of HIV to infants. Point-of-Care Viral Load (POC VL), which allows testing to be conducted at or near… Read More
Currently, about half of patients on antiretroviral treatment have access to viral load testing; however, access remains focused within a small number of countries. To date, routine HIV VL monitoring, which is considered the best method for monitoring antiretroviral treatment, has been fully implemented in only 68% of low- and middle-income countries, and partially implemented… Read More
Scaling up viral load testing to reach the 3rd 90 of the UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets by 2020 requires a holistic approach, addressing each step of the VL testing continuum from the demand for test request for all eligible patients, to the utilization of test results. Improving VL scale-up at the facility level is important, however,… Read More
This viral load (VL) cascade self-assessment scorecard and user guide is used by the LabCoP country teams to assess the status of the different thematic areas of the VL cascade and their testing services to help identify opportunities for improvement. It was designed by the LabCoP team with assistance from Global stake holders to address… Read More
In September 2018, Solange Baptiste and Helen Etya’ale from International Treatment Preparedness Coalition (ITPC) presented about HIV viral load testing (VLT) demand creation. These presentations contain helpful information that country teams can use to improve demand creation for their HIV VLT programs. This includes information about the significance of demand creation for VLT and the… Read More
WHO has updated its Essential Diagnostics List, a catalogue of the tests needed to diagnose the most common conditions as well as a number of global priority diseases.
Integrating testing using multiplex technologies at the appropriate level of care can lead to more efficient and cost-effective testing services and can help to simplify and streamline other systems, such as specimen referral, human resources, and quality assurance. Integration should be a priority for both those countries with currently operational multi-disease testing devices and those… Read More
This Rapid Testing Continuous Quality Improvement (RTCQI) training video and competency assessment tool is available on a free virtual education platform, PEPconnect to assist ministries of health, health-care providers, and stakeholders in planning, implementing and sustaining quality assurance for point-of-care testing. Critical for the first of UNAIDS’ 90-90-90 targets, this platform is developed by the… Read More
Kenya’s presentation during the May LabCoP ECHO session included their experiences implementing the ‘Plan, Do, Study, Act’ (PDSA) cycle to prioritise and rapidly test ‘change ideas’ needed to facilitate the rapid identification of unsuppressed viral load, followed by swift appropriate clinical action.
This four-step overview of Laboratory African Regional Collaborative (LARC) was presented by Patricia Riley from the International Laboratory Branch of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. LARC can be used by countries to address inefficiencies at the laboratory–clinical interface at clinic level, and achieve the 3rd ‘90’ of the UNAIDS 90-90-90 HIV targets.
This presentation by Dr. Ritu Shrivastava from the International Laboratory Branch of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention covers free online, didactic and in-person resources available for global system strengthening through three public-private partnerships (PPP). These partnerships between the President’s Emergency Plan For AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and three private entities (Becton Dickinson and… Read More
In 2013, the World Health Organization recommended viral load (VL) monitoring as the gold standard for monitoring the effectiveness of antiviral therapy (ART). One of the key barriers to VL testing in resource-limited settings is the lack of efficient specimen transport systems, to allow plasma or whole blood samples to reach the testing laboratories in… Read More
The Stronger Together public-private partnership between Siemens Healthineers and PEPFAR is institutionalising quality improvement via a free e-platform, PEPconnect, through this library of 48 videos (with a total viewing time of 14.5 hours) that capture the lectures from the 9-day classroom-based Quality Control and Method Validation course. The course is designed to enable the participants… Read More
Early infant diagnosis (EID) is critical for timely initiation of antiretroviral treatment (ART) in HIV-infected children who are at high risk of mortality. In recognition of the immense benefits of dried blood spot (DBS) as a means of increasing the access to EID, the World Health Organization, African Society for Laboratory Medicine, Centers for Disease… Read More
The Laboratory African Regional Collaborative (LARC) project supports clinicians, laboratorians and data record units to work together and improve the proportion of viral load test results put in patients’ files. LARC is a useful tool that can be used by countries to address inefficiencies at the laboratory-clinical interface at clinic level, and achieve the 3rd… Read More
This review article identifies the benefits, enabling factors, and associated challenges for public and private sectors to engage in public-private partnerships. These partnership contributions to laboratory systems strengthening are a model, and present opportunities that can be leveraged to strengthen systems to accelerate the scale up of Viral Load and Early Infant Diagnosis to achieve… Read More
This supplement, produced by Labs for Life, a public-private partnership between Becton Dickinson, Company and The President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), was published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases. This supplement is designed to support Ministries of Health, Laboratory Experts, Clinical staff, and implementing partners to improve global laboratory systems. This is accomplished… Read More
This course provides key information on safe practices, infection control, personal protective equipment, pre- and post-exposure prophylaxis, and ways to manage and dispose of health care waste properly. The goal is to familiarize Clinical health care workers with proper safety practices and help them: Protect themselves and their coworkers Protect patients and clients Protect the… Read More
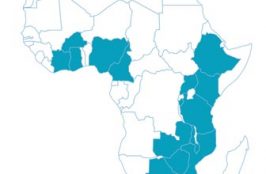
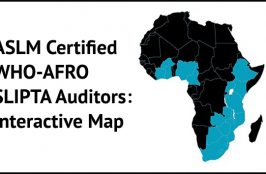
ASLM has been designated by WHO-AFRO to coordinate and lead the implementation of the Stepwise Quality Laboratory Improvement Process towards Accreditation (SLIPTA) in Africa. ASLM has developed a standardized SLIPTA auditor training curricula and trained the auditors at country and regional levels. This map shows the number of ASLM certified SLIPTA auditors per country.
This insightful paper was published in Plos about the missed potential of CD4 and viral load testing to improve clinical outcomes for people living with HIV in lower-resource setting
WHO-AFRO has established the Stepwise Laboratory Quality Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (SLIPTA) programme, a framework for improving the quality of public health laboratories in developing countries to achieve ISO 15189 standards. Through standardised processes, SLIPTA measures and evaluates the progress of laboratory systems towards international accreditation and awards a certificate of recognition (0-5 stars rating)…. Read More
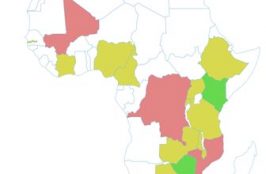
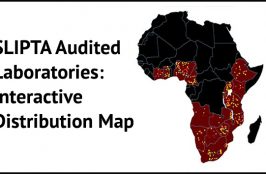
ASLM has created a database of internationally accredited medical laboratories in Africa, plotted on this map. Data were collected from accreditation agencies and on-line sources, as well as through communications with Ministry of Health focal persons, ASLM Ambassadors, and program leaders in each country.
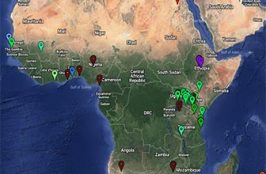
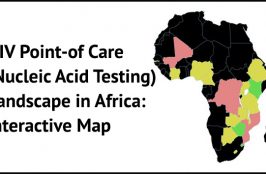
Strategic deployment of POC EID is key to getting more infants tested for HIV and initiated on treatment in a timely manner. This map indicates the distribution by type and numbers of POC Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) for HIV, EID and VL technologies ( Alere, Samba, GeneXpert, etc. ) being used by some countries in… Read More
In collaboration with ASLM and the LabCoP community, the CDC International Laboratory Branch (ILB) presented the 3rd of 6 ECHO sessions dedicated to waste management. In this session, a draft of a viral load waste management checklist tool that can be used as baseline audit of select country VL labs was introduced. The tool aims… Read More
In collaboration with the African Society for Laboratory Medicine (ASLM) and the LabCoP community, the CDC International Laboratory Branch (ILB) presented the 1st of 6 ECHO sessions dedicated to waste management. In this session we reviewed waste management at the country level using the responses to the November 2018 LabCoP Waste Management Questionnaire. In addition,… Read More
In collaboration with ASLM and the LabCoP community, the CDC International Laboratory Branch (ILB) presented an overview of the World Health Organization (WHO) Publication: ‘Safe Management of Wastes from Health-Care Activities’ during the 2nd of 6 ECHO sessions dedicated to waste management. This document, developed by WHO in 2017, highlights the key aspects of safe… Read More
This document, developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2017, highlights the key aspects of safe healthcare waste management in order to guide policymakers, practitioners and facility managers to improve such services in healthcare facilities. It is based on the comprehensive WHO handbook ‘Safe Management of Wastes from Health-Care Activities’ (WHO, 2014), and also… Read More
The waste produced in the course of healthcare activities, from contaminated needles to radioactive isotopes, can cause infection and injury. Inadequate waste management is likely to have serious public health consequences and deleterious effects on the environment. The resources linked here and this downloadable handbook published by the World Health Organization (2014), provide comprehensive guidance… Read More
The VL/EID ISME Reference Manual published by PEPFAR and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is a guide for Implementation Subject Matter Experts (ISMEs) who offer either in country or remote technical assistance in VL/EID scale-up. Collectively, it presents best practices and proposed solutions for the challenges that are common across PEPFAR programs. This… Read More
LabCoP members who attended the Kampala face-to-face meeting in October 2018 developed a Decision-Making Matrix that outlines strategic areas, strategic options, and priority action items for improvement in four focus areas within the viral load cascade, including demand creation, results utilization, waste management and biosafety, and network optimization. This matrix could be used as a… Read More
which provides results within minutes of testing, has overcome some major obstacles to treatment, giving hope to thousands of mothers and their families. UNICEF learned how point-of-care helped a Cameroonian mother named Antoinette. After losing her husband to an AIDS-related illness, she was determined to keep her children healthy and HIV-negative. UNICEF produced the video… Read More
Several new laboratory technologies are available or are being developed to allow for testing of different conditions using disease-specific tests on the same platform. For example, a single device may be able to test for the presence of tuberculosis (TB) and HIV, and quantitatively measure HIV and hepatitis C viral load by using disease-specific reagents… Read More
This publication provides high-level guidance on implementing and scaling up HIV viral load testing programmes for health ministries and implementation partners, using a three-phased approach: (1) planning; (2) scale-up; and (3) sustainability. The guidelines for managing antiretroviral therapy (ART) issued by WHO have recognized the importance of viral load monitoring since 2003. Routine viral load… Read More
Treatment initiation ART should be initiated in all children, adolescents, pregnant and breastfeeding women and adults living with HIV, regardless of WHO clinical stage and at any CD4 cell count. ART should be initiated in all children, adolescents, pregnant and breastfeeding women and adults living with HIV, regardless of WHO clinical stage and at any… Read More
The 2013 WHO consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection recommend viral load as the preferred monitoring approach to diagnose and confirm ART failure. As countries invest in the scale-up of routine viral load testing, it is critical to measure the impact and progress towards achieving the UNAIDS… Read More
Based on the recent encouraging evidence POC/ near-POC EID warrants consideration of rapid adoption and strategic scale up of this solution complementing the existing laboratory network. Ravikiran Bhairavabhotla from CDC briefly outlines the evidence and tools to support the strategic introduction of POC EID as part of a tiered national laboratory network.
Sufficient evidence has been generated on the performance of these assays in the intended field settings to support rapid national regulatory approval and initiation of scale-up. Performance was consistent between laboratory and field settings, and across countries. Further technical evaluations of these technologies are unlikely to add value, but may instead delay implementation and timely… Read More
Because of the high risk of death before the age of 2 years among HIV-infected infants, and given the increasing availability of paediatric antiretroviral treatment in many resource-limited settings, WHO recommends that national programmes should establish the capacity to provide early virological testing of infants for HIV.
To reduce morbidity and mortality among HIV-infected children and close the treatment gap for HIV-infected children, there is an urgent need to evaluate existing programmatic and laboratory practices for early infant diagnosis and introduce strategies to improve identification of HIV-exposed infants and ensure access to systematic, early HIV testing, with early linkage to treatment for… Read More
In this Malawi study, ART initiation rates were significantly improved with the implementation of same-day POC EID testing compared with referred, longer-turnaround laboratory-based testing.
In this cluster-randomized controlled trial, Jani et al. evaluated the effect of point-of-care (POC) early infant HIV testing on rates of antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation and retention in care among HIV-positive infants who presented for early infant diagnosis at health facilities in Mozambique. POC achieved more rapidly diagnosis and timely provision of treatment to HIV-infected… Read More
A real life story of how of POC EID devices strategically placed at the point where they are direly needed testing for HIV exposed infants in Malawi, are great impact for the infants and their families. Infants born to or breastfed by HIV positive mothers are in need of timely HIV because risk of mortality… Read More
Ndlovu and colleagues demonstrated the feasibility of the GeneXpert multi-disease testing at the near point of care in district and subdistrict health settings in Zimbabwe
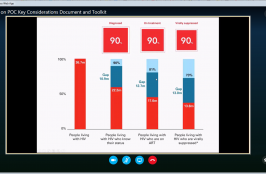
On 15 May, 2018 UNICEF hosted a webinar to provide a broad overview of the Key Considerations Document and the HIV POC Diagnostics Toolkit and to promote coordinated dissemination of both resources amongst partners at the country level. Click the player to watch the webinar.
An extension of Key Considerations for Introducing New HIV Point of Care Diagnostic Technologies in National Health Systems, this Toolkit contains various practical tools and guidance to support countries as they introduce point-of-care (POC) HIV technologies into existing national diagnostic networks and laboratory systems. It provides a roadmap for countries as they seek to expand… Read More
Point-of-Care Testing: Why is it important? Imagine yourself in a city at the centre of one of the world’s deadliest disease outbreaks. You watch as your friends and relatives are struck down by an aggressive illness that kills roughly 50-90% of those affected. One evening, you go to bed tired and achy, awakening the next… Read More
Representatives from the African Society for Laboratory Medicine (ASLM), UNICEF and the Clinton Health Access Initiative, Inc. (CHAI) came together 17-18 August 2017 in New York City, United States, to review progress to date on the implementation of a joint point-of-care project and to refine coordination mechanisms to achieve greater impact. “This project has… Read More
Broadens access to HIV viral load monitoring On July 20, 2017, Cepheid received World Health Organization (WHO) prequalification for its Xpert® HIV-1 Viral Load (VL) test. The Xpert® HIV-1 VL test measures Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA in human plasma from individuals infected with HIV-1 in less than 90 minutes. Measurement of blood… Read More
Gebremicael, et al. report results from a technical evaluation of the BD FACSPresto Point-of-Care CD4 platform in Ethiopia using capillary and venous blood samples. Researchers found acceptable agreement with conventional systems for measuring CD4 count, CD4% and Hgb concentration. This paper was published in April 2017 by PLOS ONE.
Vojnov, et al., present results from a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the benefit of using short message service (SMS) and general packet radio service (GPRS) printers to increase the efficiency of early infant diagnosis (EID) test result delivery compared with traditional courier, paper-based result delivery methods. The authors found that SMS/GPRS result delivery… Read More